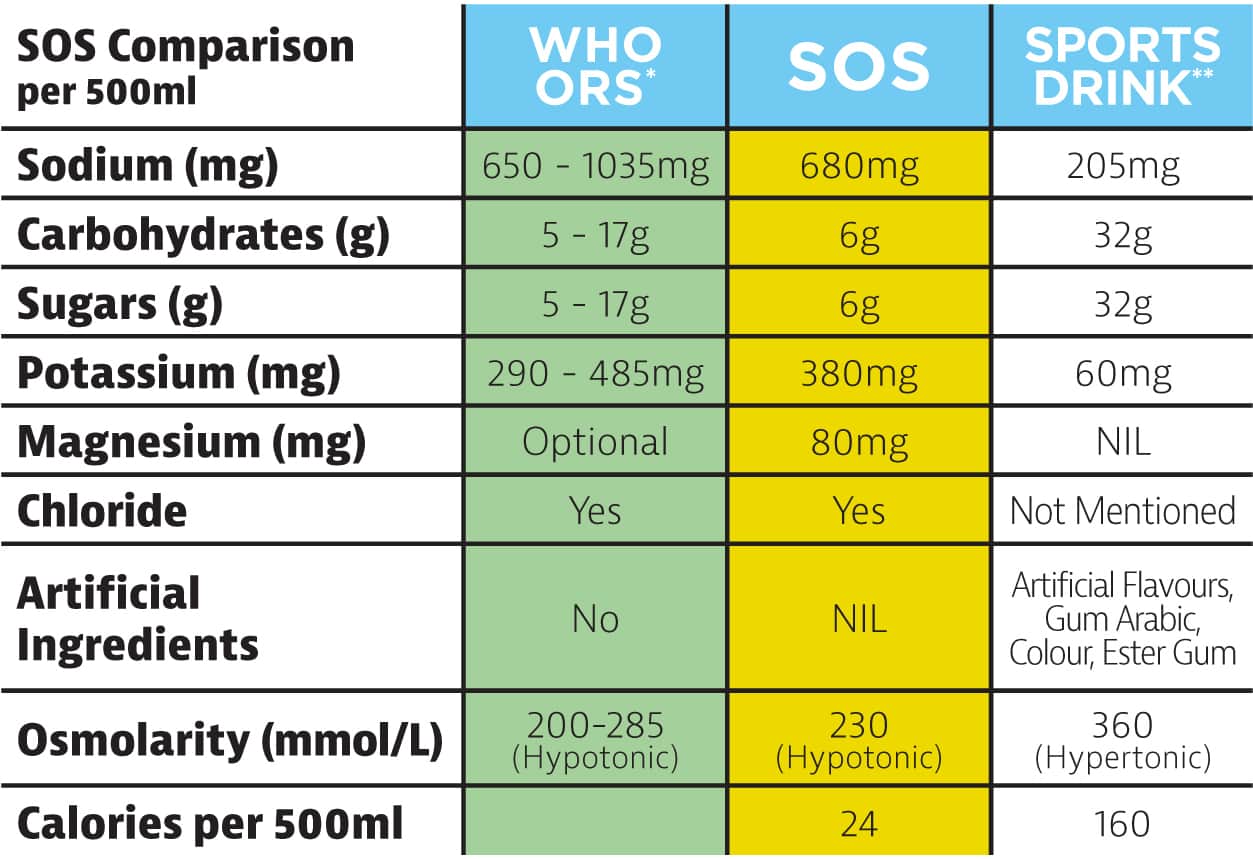
In order to aid the absorption of water, sodium and a small amount of glucose (sugar) work together in the gastro-intestinal system. This occurs through the Sodium : Glucose co-transport system in the small intestine. When a molecule of glucose crosses the membrane from the small intestine into the blood stream a molecule of sodium binds to it and crosses also. Through osmotic forces water will follow sodium and through this process facilitate the water being absorbed into the blood stream to maintain blood volume and allow the body to continually cool itself.
Potassium further assists with sodium regulation in the body also.
Knowing that glucose is necessary in small amounts for optimal absorption may change the way you look at completely sugar free options that invaribly use artificial sweeteners for flavour and are not able to have the same benefits of absorbtion.
Sports drinks typically contain too much glucose (sugar) and not enough sodium to facilitate this process. The large amount of sugar in sports drinks can often slow gastric emptying whilst exercising, leading to a bloated feeling as the fluid will not move through the gut. Not only is this uncomfortable but it also inhibits the absorption rate of the fluid.